
To determine: The new placement of departments that will minimize the total transportation costs.
Introduction:
Product layouts:
Product layout is a production system where the equipment and workstations are placed along the production and assembly lines. A conveyor is used to move the production units along the line. Product layouts have specialized labor to perform specific functions with the help of equipment (programmed to do a specific tasks in a repetitive manner). The layout is mostly based on the processing sequence.
Process layouts:
Process layout is a production system where the equipment is placed in a system based on their functions. The production line is planned to eliminate wastes. In certain process layouts, the machineries and work settings are not arranged as per the standardized production sequence. However, there would be an assembly having similar machineries and operational activities depending on the requirement. For example, paint department.
Answer to Problem 15P
Arrangement:
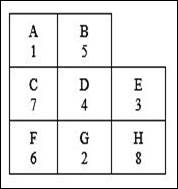
The total transportation cost for the arrangement is $143, 650 per day.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
- Work centers 1 and 3 are assigned in two locations and cannot be moved.
- There are 8 work centers.
- Cost is $1 per load per meter.
- The departments are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8.
- The locations are A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H.
Distances between locations (meters):
| To | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H |
| From | ||||||||
| A | 40 | 40 | 60 | 120 | 80 | 100 | 110 | |
| B | 60 | 40 | 60 | 140 | 120 | 130 | ||
| C | 45 | 85 | 40 | 70 | 90 | |||
| D | 40 | 50 | 40 | 45 | ||||
| E | 90 | 50 | 40 | |||||
| F | 40 | 60 | ||||||
| G | 40 | |||||||
| H |
Number of load per day between departments:
| To | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| From | ||||||||
| 1 | 10 | 5 | 90 | 370 | 135 | 125 | 0 | |
| 2 | 360 | 120 | 40 | 115 | 45 | 120 | ||
| 3 | 350 | 110 | 40 | 20 | 190 | |||
| 4 | 190 | 70 | 50 | 200 | ||||
| 5 | 10 | 40 | 10 | |||||
| 6 | 50 | 20 | ||||||
| 7 | 20 | |||||||
| 8 |
Locations:
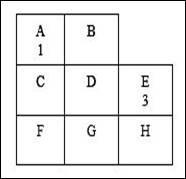
Arrangement of departments:
The numbers of trips between work centers is shown and are ranked from high to low.
| Work centers pair | Number of loads | Ranking |
| 1–2 | 10 | |
| 1–3 | 5 | |
| 1–4 | 90 | 11 |
| 1–5 | 370 | 1 |
| 1–6 | 135 | 6 |
| 1–7 | 125 | 7 |
| 1–8 | 0 | |
| 2–3 | 360 | 2 |
| 2–4 | 120 | 8 (Tied) |
| 2–5 | 40 | |
| 2–6 | 115 | 9 |
| 2–7 | 45 | |
| 2–8 | 120 | 8 (Tied) |
| 3–4 | 350 | 3 |
| 3–5 | 110 | 10 |
| 3–6 | 40 | |
| 3–7 | 20 | |
| 3–8 | 200 | 4 |
| 4–5 | 190 | 5 (Tied) |
| 4–6 | 70 | 12 |
| 4–7 | 50 | |
| 4–8 | 190 | 5 (Tied) |
| 5–6 | 10 | |
| 5–7 | 40 | |
| 5–8 | 10 | |
| 6–7 | 50 | |
| 6–8 | 20 | |
| 7–8 | 20 |
The table clearly indicates that work centers 1-5 have the highest number of trips between them. After that the following work centers have the most number of trips: 2-3, 3-4, 3-8, 4-5, 4-8, 1-6, 1-7, 2-4, 2-8 and others. After continuous trial and error method the following assignment is reached. It is to be noted that, except the pre assigned work centers, slight variations are reasonable in the assignment as long as work centers 2,4 and 8 are nearer to 3, 4 is nearer to 5 and 5 is nearer to 1.
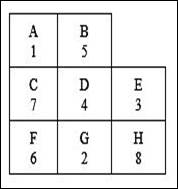
Calculation of cost for each work center pair:
The cost for each department pair is calculated by multiplying the number of loads with the distance with the cost per load per meter.
Department 1-2:
Department 1-3:
Department 1-4:
Department 1-5:
Department 1-6:
Department 1-7:
Department 2-3:
Department 2-4:
Department 2-5:
Department 2-6:
Department 2-7:
Department 2-8:
Department 3-4:
Department 3-5:
Department 3-6:
Department 3-7:
Department 3-8:
Department 4-5:
Department 4-6:
Department 4-7:
Department 4-8:
Department 5-6:
Department 5-7:
Department 5-8:
Department 6-7:
Department 6-8:
Department 7-8:
Calculation of total cost:
The total cost is calculated by adding the cost of individual work center pairs.
The total transportation cost for the arrangement is $143,650.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Operations Management
- 5 departments are to be assigned to locations B-F in the grid. (For technical reasons, department 6 must be assigned to location A). Transportation cost is Rs.3 per foot. Information on interdepartmental work flows and distances between locations is shown in the following tables. Develop a suitable layout that minimizes transportation costs using the given information. Compute the total cost. Assume the reverse distances are the same. From Distance between Locations (Feet) To A B D E F A 70 120 70 100 150 70 110 60 90 160 80 70 D 70 140 E 70 F From Distance between Locations (Feet) To 2 4 115 52 54 15 40 2 10 16 44 3 2 20 13 2 6 A Dept. 6 B D E Farrow_forwardConsider the relationship chart for the a fast-food restaurant, Assume that the areas required for each department are: Department Area Required (Square feet) (CB) 300 (CF) 200 (PS) 200 (DD) 200 (CS) 300 Assume facility dimension of 6 (horizontal) by 8 (vertical) squares, where each square is 5 feet on a side. As a result, for example the CB department requires 12 squares. Develop a layout for the fast-food restaurant.arrow_forwardHren Electronics is in process of setting a new office building. The following tables show the number of expected communications among the four departments and two possible layouts for considerations (tables 2 and 3 show the distance among the departments in the given layout). Calculate a total cost (or total distance traveled) for each layout and provide a recommendation that would minimize the total costs. Table 1. Number of transactions A B C D A 0 75 20 0 B 5 0 300 100 C 10 0 0 0 D 0 20 0 0 Table 2. Layout 1 (Walking distance in meters) A B C D A 0 10 20 30 B 10 0 10 20 C 20 10 0 10 D 30 20 10 0 Table 3 Layout 2 (Walking distance in meters) A B C D A 0 5 30 40 B 5 0 5 20 C 30 5 0 20 D 40 20 20 0arrow_forward
- 4. An industrial engineer has conducted a study aiming to minimize traffic flow between the work stations (WSS) encoded as A, B, C, D, and E. The current layout of the work stations having equal sizes is illustrated below. At the current plan, work station B locates at the center. Distances between the WSS are also presented at the same figure (For instance, the distance between A and B is 3m while it is 4m between B and D. Additionally, C and D are 5m far away from each other.). Calculate the weighted distance of the current layout plan, then propose a new plan and compare the plans. A 5m 5m 11 D 4m +3m E 5m 5m Number of loads flowing between the WSS A D 40 WS SABCDE А B 10 C 50 25 . 10 25 E 35 15 20 20 -arrow_forwardWhat is facility layout? Choose a business that you would be interested in opening in your community. How would you decide where to locate that business? What would you be most concerned about in making this choice?arrow_forwardGator Offi ce Systems is comparing two layouts for thedesign of its offi ce building. It has interviewed managers inorder to develop the from–to matrix shown in Table 10-12. Th etwo layouts considered are shown in Figure 10-14. Which layoutdo you think is better for Gator Offi ce Systems, using the load–distance model?arrow_forward
- What layout type is a conventional supermarket and how does it differ from a manufacturing operation using the same layout type?arrow_forwardMunson Manufacturing, in Gainesville, Florida, wants to arrange its four work centers so as to minimize interdepartmental parts handling costs. The flows and existing facility layout are shown in the figures below. Figure 1. Parts Moved Between Work Centers A D A 450 600 50 350 200 725 D Figure 2. Existing Layout A B -30 -30 -30 a) For the existing layout, the cumulative "load x distance" or "movement cost" = feet (enter your response as a whole number).arrow_forwardMunson Manufacturing, in Gainesville, Florida, wants to arrange its four work centers so as to minimize interdepartmental parts handling costs. The flows and existing facility layout are shown in the figures below. Figure 1. Parts Moved Between Work Centers A AB с D Figure 2. Existing Layout A B -30¹- -30¹- C 350 0 0 -30¹- D B 480 00 0 0 a) For the existing layout, the cumulative "load x distance" or "movement cost" = whole number). с 600 175 The cumulative distance based on the overall movement of parts between work centers for this layout=feet (enter your response as a whole number). 0 D 50 0 750 feet (enter your response as a will be next to each other as they have the highest number of moves between each other. Based on the flows shown in the matrix, one should expect that the centers A and Based on the flows shown in the matrix, one should expect that centers Cand will be next to each other as they have the second highest number of moves between each other. b) The aim is to…arrow_forward
- Identify the manufacturing layout type. Give justification for selecting such typearrow_forwardExplain what are the various steps in developing a cellular manufacturing layout?arrow_forwardLayout planning involves decisions about the physical arrangement of economic activity centres within a facility. With reference to the organization of your choice discuss the advantages and disadvantages of the particular layouts that are employed and evaluate why these layouts are appropriate?arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.
Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.





